Vinayak Agarwal | Professor Ravi Kothari | Unstructured Information Processing
Person Detection using Faster-RCNN
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Abstract
Dataset
Annotation
Pre-processing
Methodology:
Faster-RCNN
Non-max suppression
Anchors
Results
Future work
Bibliography
Abstract
Person detection has been a widely researched topic in the field of Computer Vision and
Artificial Intelligence. It has multiple applications like target detection or traffic/crowd control.
From image processing to deep learning, person detection techniques have improved both in
accuracy and response time. This paper is an attempt to detect people from images using
Faster-RCNN and replicate results of existing research. In order to verify advantages of deep
learning techniques over HOG with SVM, a HOG-SVM model was built to run the test images
on. Amongst deep learning approaches, while YOLO has proven to be the fastest,
Faster-RCNN has been very accurate and computationally feasible for industrial approach.
Dataset
The INRIA person dataset was used for training and testing. The Penn-Fudan Database for Pedestrian Detection and Segmentation was used to augment the training data and make the model more robust.
Annotation
The images had been annotated as per the PASCAL VOC dataset format. Regex expression were run across each annotation file for an image and a JSON file was created which contained every filename along with the coordinates of the ground truth boxes. The json file was then used to create a text file with the following format: _Filepath,x1,y1,x2,y2,class_name where,
● filepath is the path of the training image
● x1 is the xmin coordinate for bounding box
● y1 is the ymin coordinate for bounding box
● x2 is the xmax coordinate for bounding box
● y2 is the ymax coordinate for bounding box
● class_name is the name of the class, i.e., human in that bounding box_
Pre-processing
● The shortest side of the image was resized to 600px
● All images were horizontally flipped for data augmentation
● Reducing image size led to loss of information and hence was not applied.
● Converting all images to grayscale also led to loss in accuracy and hence was not applied in the final
dataset.
Methodology:
Faster-RCNN
● Take an input image and pass it to the ConvNet which returns feature maps for the image
● Apply Region Proposal Network (RPN) on these feature maps and get object proposals
● Apply ROI pooling layer to bring down all the proposals to the same size
● Finally, pass these proposals to a fully connected layer in order to classify any predict the bounding
boxes for the image
Non-max suppression
In-order to deal with overlapping bounding boxes, non-max suppression is applied.
Anchors
● Anchor scales used : 128x128, 256x256, 512x
● Anchor ratios : 1:1, 1/√2:2/√2, 2:√2:1/√
● Total number of anchors: 9
● Since stride taken was 16, at every 16 pixels, 9 anchor boxes were considered for occurence of object
Results
The accuracy of the RPN bounding box was : 93.17%

The following is the rate of growth of accuracy with the number of epochs:
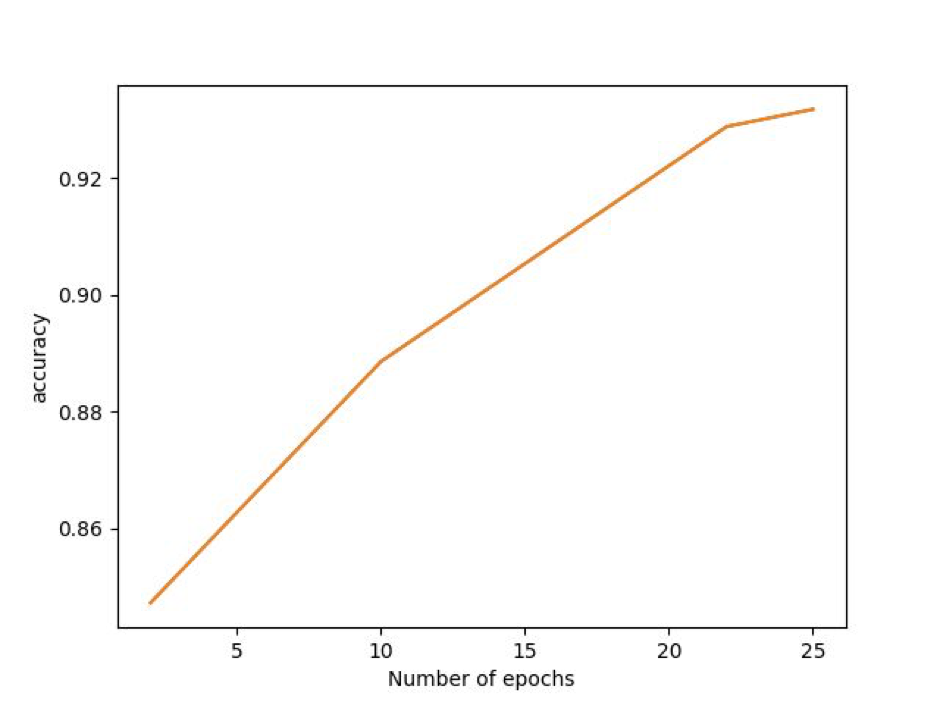
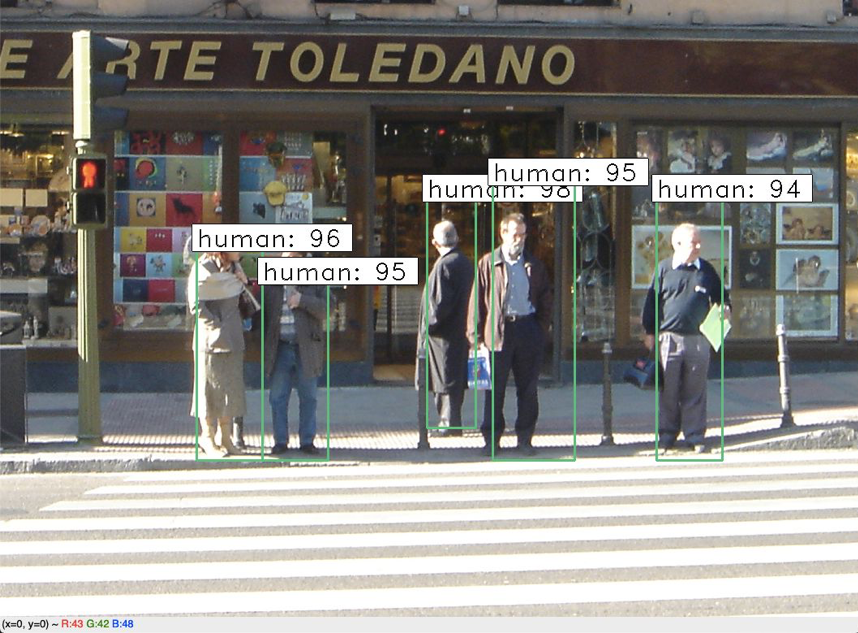
The following are the classification results:

Future work
● A few of the training images had more than one person. Due to the annotation limitations, only
one bounding box coordinates could be provided to the model. Since the model treats all the
data outside the bounding box as negative samples, there might be the case that a few images of
people were assumed to be negative sample. Such samples might have affected the accuracy of
the model.
● I recently came across a paper ( Martinson, E., and V. Yalla. "Real-time human detection for robots
using CNN with a feature-based layered pre-filter." _Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN),
2016 25th IEEE International Symposiumon_ . IEEE, 2016.) which provides the neural net training images
after applying HOG on them to extract relevant features. I would like to try such preprocessing to my model.
Bibliography
● Literature Review
○ Girshick, Ross. "Fast r-cnn." Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision . 2015.
○ Redmon, Joseph, et al. "You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection." Proceedings of the
IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition . 2016.
○ He, Kaiming, et al. "Deep residual learning for image recognition." Proceedings of the IEEE conference
on computer vision and pattern recognition . 2016.
○ https://medium.com/@smallfishbigsea/faster-r-cnn-explained-864d4fb7e3f
○ https://towardsdatascience.com/fasterrcnn-explained-part-1-with-code-599c16568cff
○ https://medium.com/@madhawavidanapathirana/https-medium-com-madhawavidanapathirana-real-time-human-detection-in-computer-vision-part-1-2acb851f4e
○ https://medium.com/@madhawavidanapathirana/real-time-human-detection-in-computer-vision-part-2-c7eda27115c
● Code References:
○ https://github.com/kbardool/keras-frcnn
○ https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2015/02/16/faster-non-maximum-suppression-python/
● Datasets
○ http://pascal.inrialpes.fr/data/human/
○ https://www.cis.upenn.edu/~jshi/ped_html/